The Untold Adventures of Charles Babbage: A Journey Through Time
Written on
Chapter 1: Early Life and Remarkable Inventions
Charles Babbage, often referred to as the Father of modern computing, was born in London in 1792. From a young age, he exhibited remarkable aptitude for mathematics and later pursued advanced studies at Trinity College, Cambridge. A true polymath, Babbage's interests spanned mathematics, philosophy, and mechanical engineering. Throughout his career, he experimented with various inventions, including a seismograph, a black box for trains, and an altitude meter.
Babbage's curiosity led him to extreme experiments; for instance, he famously lowered himself into a volcano and subjected himself to temperatures of 265°F to study their effects on the human body. He even authored a book detailing how to prepare food on the moon.
Section 1.1: The Difference Engine
As Babbage's fascination with statistics grew, he began to develop ideas for a mechanical calculator. His ability to analyze vast amounts of data enabled him to uncover patterns in various fields, from zoo statistics to factory glass breakages. Collaborating with John Herschel, son of the renowned astronomer William Herschel, Babbage worked on accurately plotting latitude and longitude for maritime navigation. This collaboration brought him closer to realizing his vision of a mechanical calculator. In 1822, he presented his concept of the Difference Engine to the Royal Astronomical Society, proposing a machine capable of performing addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division automatically. His prototype garnered attention, assisting him in securing funding from the British government, although he underestimated the costs involved.
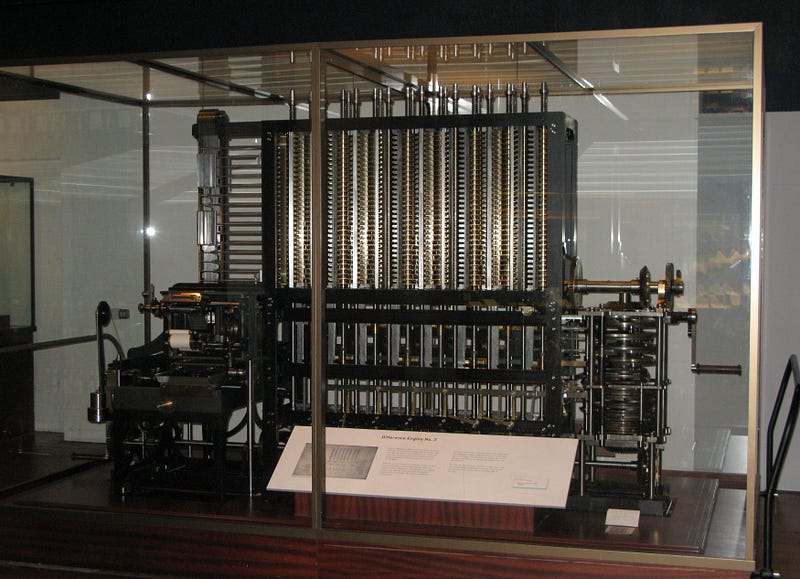
Chapter 2: A Shift in Focus
Despite his initial enthusiasm, Babbage's interest in the Difference Engine waned, leading him to pursue other projects that diverted his attention and resources. He explored the use of hydrogen blow lamps to add color to ballet costumes and introduced the penny post system, which standardized postal charges regardless of distance. This innovation proved profitable for the Royal Mail.
Babbage faced numerous personal challenges during the development of the Difference Engine, including conflicts with the scientific community that consumed valuable time. Appointed as the professor of Mathematics at Cambridge University, a position once held by Sir Isaac Newton, Babbage never delivered a single lecture throughout his 11-year tenure, claiming that his focus remained on his invention. Critics viewed this as an abuse of his position.
His political aspirations also fell short, and as the government grew impatient over the lack of progress on the Difference Engine, they began to cut funding. By this point, the expenditure on Babbage's project had reached the equivalent of two battleships. His continuous revisions and enhancements to the design of the Analytical Engine only further inflated costs and extended timelines. In 1842, the government ultimately terminated the Difference Engine project but offered Babbage a knighthood, which he declined.
Section 2.1: Final Years and Legacy
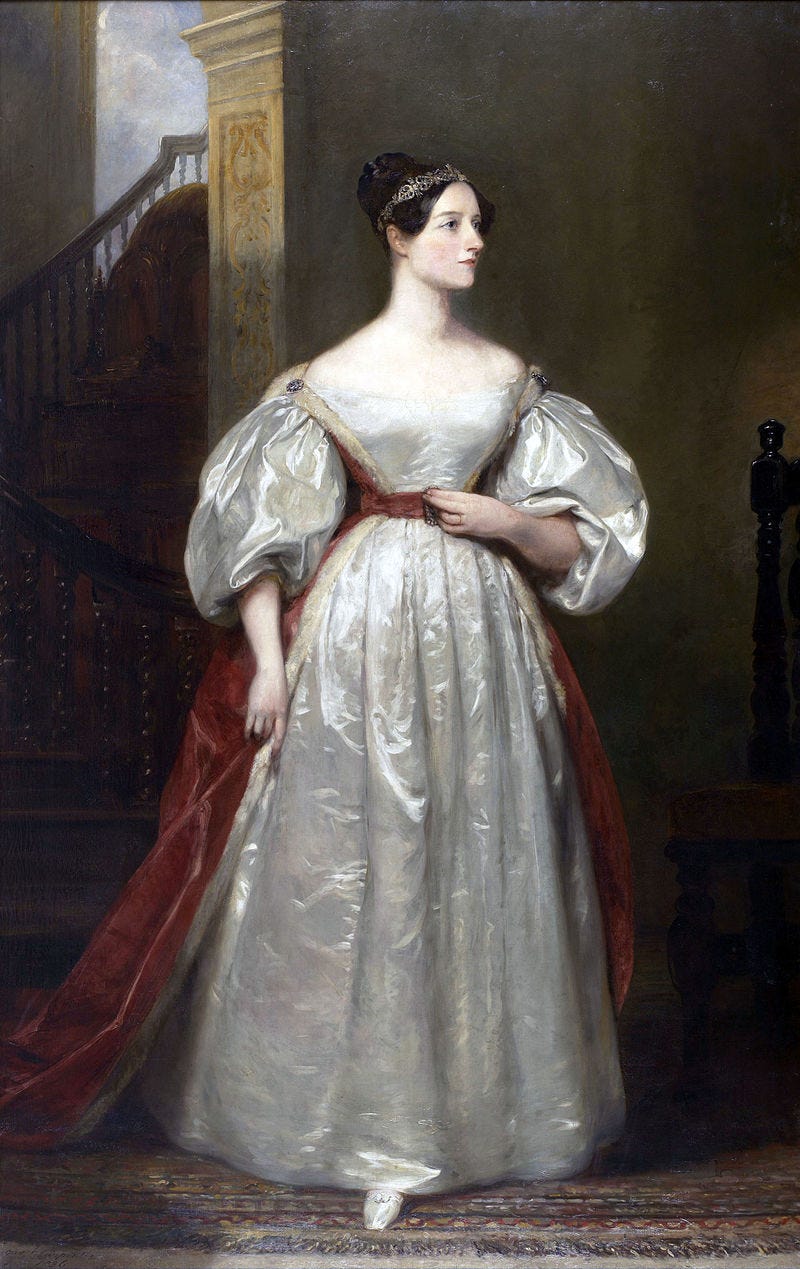

In the twilight of his career, Babbage found himself drawn into gambling, alongside the notable mathematician Ada Lovelace, resulting in significant losses for both. He insisted that a partially completed Difference Engine be displayed at the prestigious 1862 London Exhibition, but was disappointed with its placement.
Towards the end of his life, Babbage became increasingly isolated and passed away in 1871 at the age of 80. He lamented that the government should have provided him with better support to develop a functional model of the Difference Engine, believing that poor planning and distractions had ultimately thwarted his efforts. While Wilhelm Schickard, a German mathematician, created a working model of a calculating machine, it is Charles Babbage who is rightfully credited as the Father of modern computers.
Th