Mastering Linux System Performance with the 'top' Command
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to the 'top' Command
In the complex landscape of Linux system administration, the ability to monitor and assess system performance is crucial. The ‘top’ command emerges as a vital tool in this context, offering real-time insights into resource consumption and process management. This article delves into the functionalities and importance of the ‘top’ command, highlighting its role in both server and desktop environments.
Section 1.1: Overview of the 'top' Command
The ‘top’ command is an essential utility for overseeing system performance on Linux. It provides a dynamic, real-time overview of key system statistics, such as CPU load, memory usage, and active processes. With its user-friendly interface and powerful features, ‘top’ helps both system administrators and users identify performance bottlenecks, monitor resource use, and effectively manage running processes.
Subsection 1.1.1: Key Features of the 'top' Command
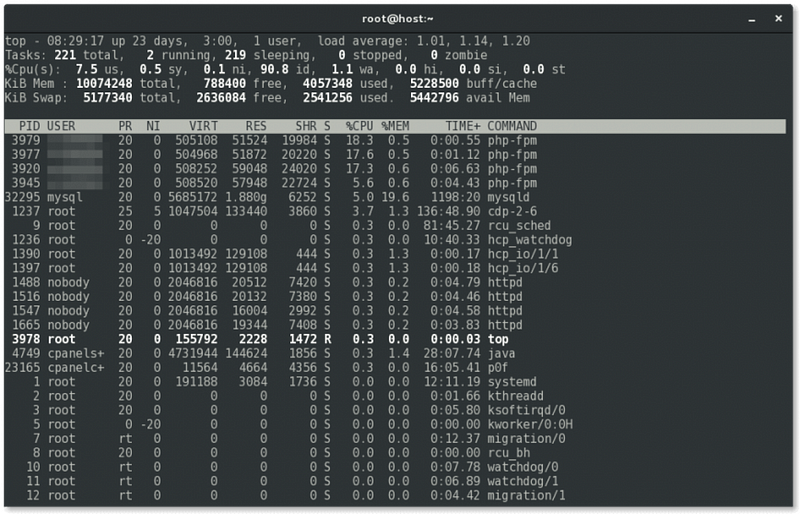
- Real-Time Updates: The ‘top’ command offers continuous updates on system resource usage, allowing users to quickly detect spikes in CPU or memory utilization, thereby enabling prompt troubleshooting.
- Interactive Interface: Its interactive nature allows users to engage with active processes, facilitating actions like sending signals, terminating processes, and adjusting their priorities.
- Resource Metrics: ‘top’ displays detailed metrics including CPU usage rates, memory consumption, and swap space utilization, providing users with an instant overview of system health.
- Sorting and Filtering: Users can arrange the list of processes based on various criteria, such as CPU load or memory usage, and apply filters to focus on specific processes.
- Process Management: The command allows users to manipulate processes directly from its interface, including sending signals like SIGTERM or SIGKILL.
- Batch Mode: The ‘top’ command can also run in batch mode, producing reports that are useful for scripting and further analysis.
- Customization Options: Users can modify the display to show or hide particular columns, tailoring the output to meet their specific requirements.
Section 1.2: Importance of the 'top' Command
The significance of the ‘top’ command in the Linux ecosystem is profound for several reasons:
- Immediate Monitoring: It provides real-time feedback on system performance, enabling administrators to quickly identify and rectify issues.
- Resource Optimization: By spotting resource-intensive processes, ‘top’ aids in optimizing the allocation of system resources, enhancing overall efficiency.
- Troubleshooting Aid: In instances of system slowdowns or bottlenecks, ‘top’ functions as a diagnostic tool, helping users pinpoint the root cause and take corrective measures.
- Effective Process Management: The command offers users the ability to manage processes efficiently, granting greater control over system functionality.
Chapter 2: Harnessing the 'top' Command for System Insights
To fully exploit the capabilities of the ‘top’ command, users can gain a deeper understanding of their Linux system's performance. Whether you are monitoring resource consumption, troubleshooting problems, or managing processes, ‘top’ stands ready to furnish the essential insights required for optimal performance.
This video, titled "Master Linux Process Management Part II," elaborates on advanced techniques for managing Linux processes, enhancing your skills with the ‘top’ command.
The second video, "Linux Performance Monitoring Tools," covers various tools for monitoring Linux system performance, providing additional context to complement the ‘top’ command.