# Understanding the Diagrams of Change: Trigrams Unveiled
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to Trigrams
The Chinese Prenatal and Postnatal Trigrams are often associated with the concepts of HeTu and LuoShu. A widely accepted narrative attributes the creation of the Prenatal Trigrams to Fu Xi. The Yi Jing, also known as the I Ching or The Book of Changes, connects Fu Xi's sixty-four hexagrams to the natural evolution of the universe, humanity, and society. Regarding the Postnatal Trigrams, there are diverse scholarly opinions, but the consensus is that King Wen of the Zhou dynasty (1099–1050 BC) was instrumental in their development.
Chapter 2: Conceptual Models of Trigrams
Building the 3-D and Spacetime Models
The models of the Prenatal and Postnatal Trigrams are derived from several key hypotheses:
- Yin and Yang are two opposing energies.
- Yang encompasses qualities like sunlight, warmth, and growth, while Yin embodies characteristics such as darkness, coldness, and decline.
- In both types of Trigrams, Yang is represented by a solid stroke "—" or a binary 1, and Yin is shown by a broken stroke "– –" or a binary 0.
- The outermost layer of each trigram is termed the "Heaven" layer, the middle layer is the "Human" layer, and the innermost layer is the "Earth" layer.
#### A. Understanding Prenatal Trigrams
In Chinese, "prenatal" translates to "before birth" or "the original state of the universe."
When examining Prenatal Trigrams, one can observe the following characteristics:
- There are four pairs of elements with contrasting qualities.
- Each element mirrors its counterpart across the center.
- The right half mirrors the left half.
- The left half, known as the Yang half, is identified by the solid stroke in the outer layer, indicating the progressive growth of Yang energy.
- The right half represents the Yin energy, where the inner layers show a decline in Yang energy.
- This system exhibits fractal properties.
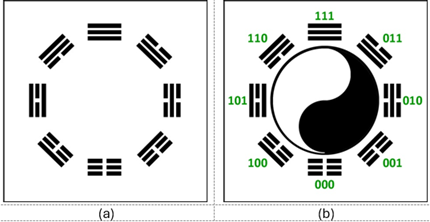
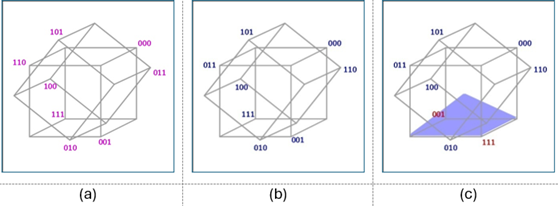
B. 3-D Model of Prenatal Trigrams
The Prenatal Trigrams share similarities with LuoShu, differing mainly in their twists. The absence of a twist indicates a less stable system with elevated energy levels. The proposed 3-D model consists of two intersecting tetrahedrons.
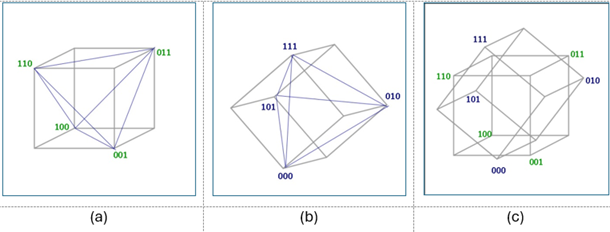
C. Spacetime Model of Prenatal Trigrams
Since the Prenatal Trigrams system is fractal, every part contains subsystems akin to the whole. The proposed Spacetime model reflects this structure, with each subsystem's cycle time being one-eighth of the overall system's cycle.
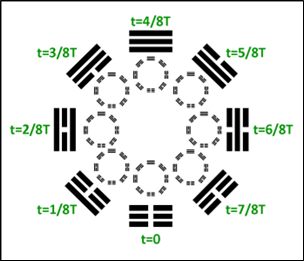
D. Prenatal Spacetime Hexagrams
Using the logic from earlier models, merging the outer and inner trigrams yields sixty-four hexagrams, termed Prenatal Spacetime Hexagrams. These hexagrams share components with Fu Xi's hexagrams, foundational to the Yi Jing.

E. Exploring Postnatal Trigrams
Constructing a 3-D model for Postnatal Trigrams presents challenges due to their seemingly less orderly nature. However, we can align them with the structure of Prenatal Trigrams for better understanding.
F. Analyzing the 3-D Model of Postnatal Trigrams
By rearranging elements in the 3-D model, we can create a structure known as PoT’. This involves applying an octahedral twist between specific elements.
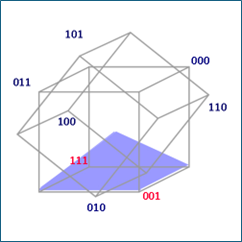
G. Constructing the 3-D Model of Postnatal Trigrams
To build this model:
- Arrange basic elements in two tetrahedrons facing each other.
- Apply twists between each element pair.
- Implement an octahedral twist to stabilize the structure.
This results in a stable configuration, illustrating how free energies can create a robust structure.
Summary
In conclusion, Postnatal Trigrams represent a stable form of Prenatal Trigrams, differing in their structural arrangement. Fu Xi’s work illustrates a system influenced solely by gravitational forces, while King Wen’s approach shows how stability can emerge from free energies through dimensional twists. The four diagrams of DOC reveal a singular system expressed in various energy states: HeTu as a crystalline form, LuoShu as a liquid-crystal structure, Prenatal Trigrams as a high-energy state, and Postnatal Trigrams as the most stable configuration.
The first video titled "Supply and Demand (and Equilibrium Price & Quantity) - Intro to Microeconomics" offers foundational insights into how supply and demand interact, affecting equilibrium price and quantity in markets.
The second video, "Change in Demand vs. Change in Quantity Demanded," clarifies the distinctions between shifts in demand and changes in quantity demanded, enhancing understanding of market dynamics.