Exploring Polkadot: A Comprehensive Overview of Its Blockchain
Written on
Introduction to Polkadot
The landscape of blockchain technology is rapidly evolving, with a growing number of innovative projects emerging. Yet, many current blockchain networks operate in isolation, making data transfer between them a significant challenge. Polkadot offers a promising solution to this issue, facilitating communication among independent blockchains. This article aims to clarify what Polkadot is, how it functions, and the potential applications it may serve in the future.
What is Polkadot?
Polkadot is an advanced blockchain platform designed to connect various blockchains, allowing them to interact seamlessly. Its goal is to foster a decentralized internet, empowering individuals by minimizing centralization. Founded by Gavin Wood, Robert Habermeier, and Peter Czaban in October 2017, Polkadot aims to revolutionize blockchain interoperability.
What Challenges Does Polkadot Address?
The main objective of Polkadot is to create a system that interlinks different blockchain networks. The founders identified a critical issue with existing blockchain architectures, particularly concerning scalability and extensibility.
Polkadot introduces a heterogeneous multichain approach, separating two core components of the consensus architecture: consensus and state communication. The current challenge lies in the fragmentation of users across multiple blockchain networks, preventing new projects from gaining the necessary traction.
A significant hurdle for new blockchains is user acquisition. A robust user base is essential for network integrity, as a limited number of validators can lead to vulnerabilities and malicious attacks. While the emergence of new blockchain projects is beneficial for the sector, it also exacerbates resource scarcity. Polkadot addresses this dilemma by enabling other blockchain systems to utilize available resources more effectively.
Essentially, Polkadot operates as a relay chain, allowing various chains to connect and enabling faster, more efficient launches. This relay chain facilitates atomic transactions between systems, significantly enhancing interoperability.
How Does the Polkadot Blockchain Function?
The Relay Chain is the heart of the Polkadot ecosystem, managing the states of connected blockchains, known as parachains. A crucial aspect of this ecosystem is its native token, DOT, which serves multiple purposes. DOT is primarily a governance token and the main currency for transactions within the Polkadot network.
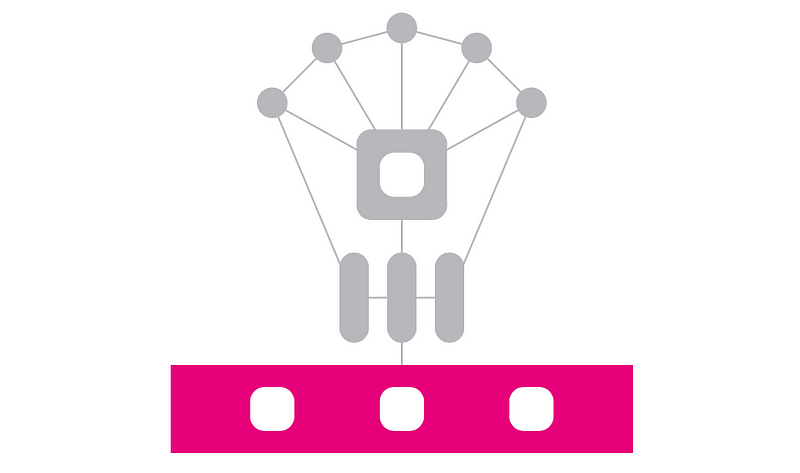
The DOT token is not capped, allowing for an annual increase of approximately 10%. Users who stake their DOT tokens to secure the network are rewarded, fostering a decentralized and robust ecosystem.
Polkadot Relay Chain: Enhancing Scalability
Polkadot aims to improve blockchain interoperability, though the Relay Chain currently accommodates around 100 parachain slots. Developers at Parity Technologies are working on nested relay chains to enhance scalability further.

Slots on the Relay Chain are auctioned off, allowing interested parties to bid for access. The bidding process is influenced by supply and demand, determining the current DOT rate. While slots are fixed for the duration of the contract, they do not yield returns like staking. However, blockchains can write their state to the Relay Chain during the contract term.
Parathreads: A Cost-Effective Alternative
Due to the potentially high costs associated with securing a parachain slot, Polkadot introduced parathreads, which allow blockchains to write data to the Relay Chain without requiring a fixed slot. Instead, transaction fees apply, influenced by network utilization.
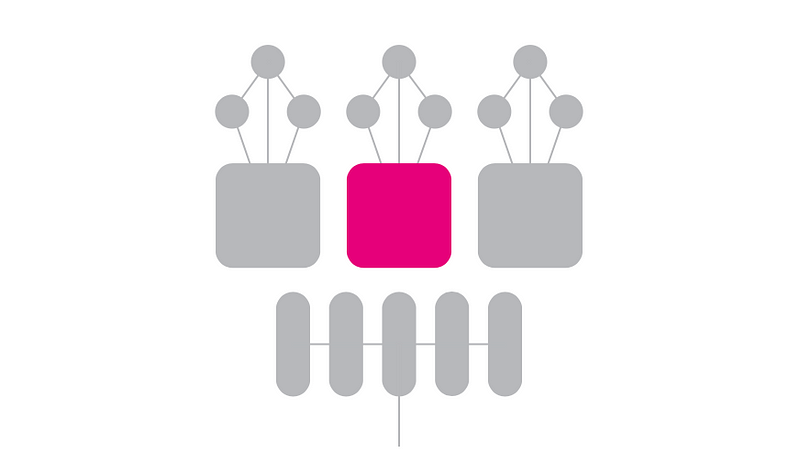
Parathreads are particularly beneficial for smaller projects, offering lower costs and maintaining high speeds through nested relay chains. Projects can switch between being a parachain or parathread based on economic considerations.
Unique Relay Chain Model of Polkadot
Polkadot's relay chain model is a distinctive feature, enabling the separation of consensus architecture, unlike other blockchains such as Bitcoin or Ethereum. While this model may seem limiting, it allows Polkadot to leverage the strengths of various connected blockchains, ensuring scalability and efficiency.
The Polkadot Token (DOT) Overview
DOT serves three primary functions within the network:
- Governance: Token holders exercise full control over network operations, similar to miners on other platforms.
- Staking: Incentives are provided for honest behavior among token holders, with rewards for positive contributions.
- Bonding: DOT must be bonded to create new parachains, decoupling old ones when tokens are removed.
Polkadot’s Approach to Interoperability
Polkadot addresses the interoperability challenges faced by established blockchains, enabling smooth communication through its relay chain. Unlike Ethereum, where oracles are necessary, Polkadot's architecture facilitates parallel transaction execution, enhancing speed and efficiency.
Bridges: Enabling Communication with Other Systems
Polkadot Bridges are specialized parachains that facilitate communication with external blockchain networks, similar to oracles in other systems.
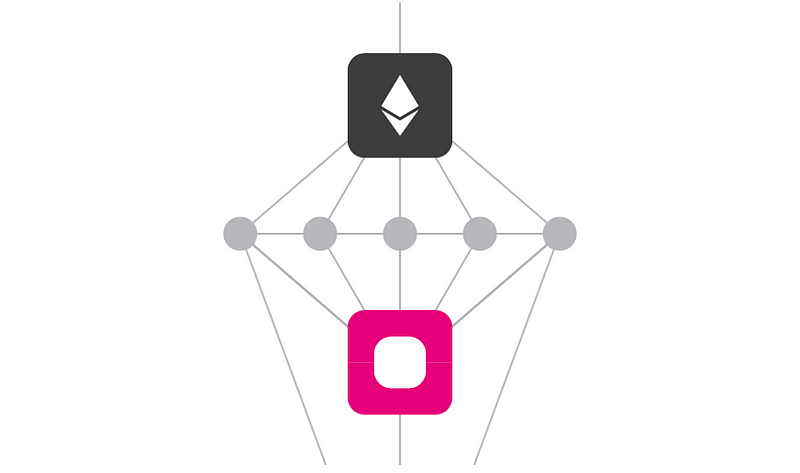
These bridges allow all blockchains within the Polkadot ecosystem to access external networks and enable seamless transactions.
Advantages of Polkadot Over Other Blockchains
The key advantage of Polkadot is its ability to connect multiple blockchains, which is particularly beneficial for decentralized trading platforms and businesses seeking interoperability. Its proof-of-stake model supports high transaction speeds and scalability.
Polkadot's strengths include:
- High scalability
- Innovative architecture for DeFi applications
- Cost-effective platform for new projects
- Bridges functioning as oracles
- Staking opportunities for DOT holders
- Affordable parathread operations
Understanding Staking on Polkadot
Polkadot employs a proof-of-stake mechanism to secure its relay chain. Currently, the inflation rate for DOT tokens is 10% annually, expected to decrease over time. A portion of staking rewards is distributed to stakeholders, with various roles available within the network.
Validators, Nominators, Collators, and Fishermen are the four main participant roles, each contributing to network security and functionality.
How to Stake Polkadot Easily
Staking Polkadot is simplified through various trading platforms. For instance, Kraken allows users to stake DOT easily, with rewards distributed bi-weekly. This convenience has made staking accessible, with returns comparable to proprietary setups.
Prominent Projects on Polkadot
Several notable projects are already utilizing the Polkadot framework, including:
- Kusama: A more experimental network akin to Polkadot.
- Edgeware: Focused on on-chain governance and compatible with Ethereum.
- Acala: A DeFi project leveraging Polkadot's capabilities for decentralized finance applications.
Conclusion: The Future of Polkadot
In summary, Polkadot stands out as a forward-thinking blockchain solution with the potential for significant impact in the industry. By addressing existing challenges and offering a scalable, cost-effective environment for blockchain projects, Polkadot may pave the way for a new wave of innovation.
The first video titled What to Expect | Polkadot Decoded 2023 provides insights into the future direction of the Polkadot ecosystem.
The second video Get Your Project Funded: Access Support Available Within the Polkadot Ecosystem discusses available resources for project funding within the Polkadot network.
FAQ
What is Polkadot?
Polkadot is an advanced blockchain platform that enhances interoperability among various blockchain networks.
Does Polkadot support oracles?
Polkadot facilitates interoperability through its Bridges, which serve a similar purpose as oracles in other systems.
What is the consensus mechanism of Polkadot?
Polkadot utilizes a nominated proof-of-stake (NPoS) consensus mechanism.
What is the purpose of the Polkadot token (DOT)?
DOT serves multiple functions, including governance, staking, and bonding for parachains.
How many DOT tokens exist?
There is no maximum supply for DOT, with annual inflation set at 10% until one billion tokens are reached.
Are there projects already operating on Polkadot?
Yes, notable projects such as Kusama, Acala, and Edgeware are currently utilizing the Polkadot infrastructure.