Setting Up Renovate Bot for GitLab: A Comprehensive Guide
Written on
Overview of Renovate Bot
In this article, I will guide you through the process of configuring Renovate Bot for GitLab. Recently, I faced a need to integrate Renovate Bot to examine private repositories, enhancing the management of project dependencies. Renovate Bot automates the scanning and updating of your codebase dependencies, alleviating the burden of manual updates, especially when dealing with numerous dependencies.
Renovate Bot is compatible with several leading CI/CD platforms like GitHub, GitLab Cloud, and Azure DevOps, making it easy to integrate into your pipelines. In my case, I utilized the self-hosted version of GitLab, which necessitates hosting the open-source Renovate Runner codebase in GitLab and triggering the pipeline on a scheduled basis. Let’s delve into the prerequisites and the steps required for implementation.
Prerequisites
To automate dependency updates via Renovate in GitLab, the following requirements must be met:
- A dedicated user account for Renovate Bot along with a generated token that has read_user, api, and write_repository permissions.
- A Renovate Bot Runner repository in GitLab.
- A project repository that includes the Renovate configuration file — renovate.json5. This file uses the JSON5 extension to allow comments within the configuration.
- A GitHub account and a generated token with API access.
Creating the Renovate Bot Service Account and Permissions
The first step involves creating a dedicated service account for the Renovate Bot. This account enables the bot to search repositories, check for dependencies, and create Merge Requests (MRs) when updates are identified. After establishing the service account, generate a GitLab TOKEN with the necessary permissions: read_user, api, and write_repository. Simultaneously, create a GitHub TOKEN with read access to fetch release notes and descriptions for the latest dependencies. While having the GitHub Token is advisable, it is not essential for the bot’s functionality.
Renovate Bot Runner Repository and Configuration
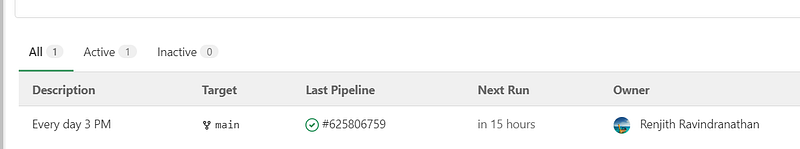
The main Renovate repository will resemble the example below. This repository houses the initial configuration and the Renovate job, which runs on a schedule, say every day at 3 PM.
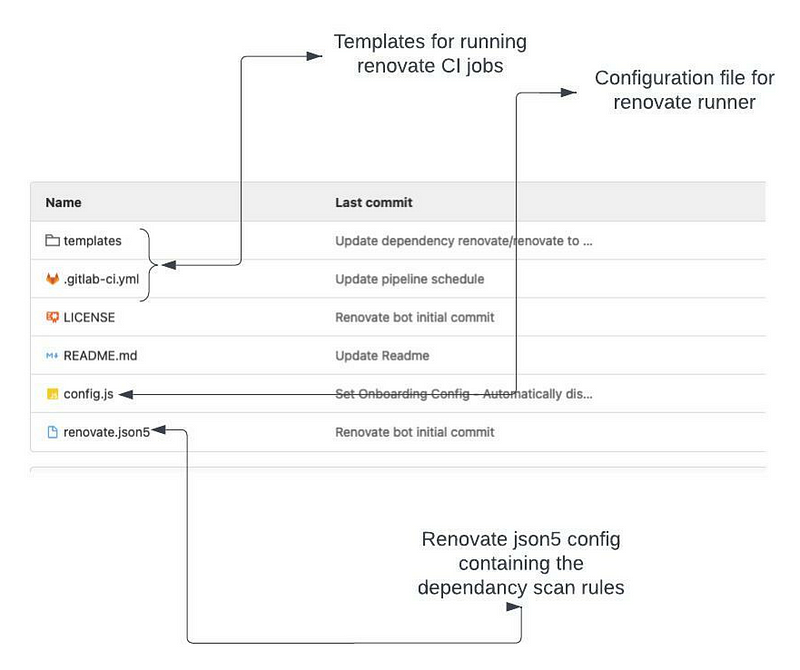
- config.js: This file includes standard configurations such as the GitLab API URL, Token, etc., necessary for the Renovate Bot.
- renovate.json5: This file specifies the dependency rules for Renovate. Each repository that requires scanning must contain this file in its root. If Renovate cannot locate this file, it will generate one automatically.
It is important to note that the renovate.json5 file exists in the main repository to facilitate self-updating of Renovate Docker images. Renovate executes scans via a Docker container, which must be kept up-to-date with the official releases. Scanning is performed through a scheduled run in GitLab CI/CD pipelines, which we will discuss next.
GitLab Pipelines
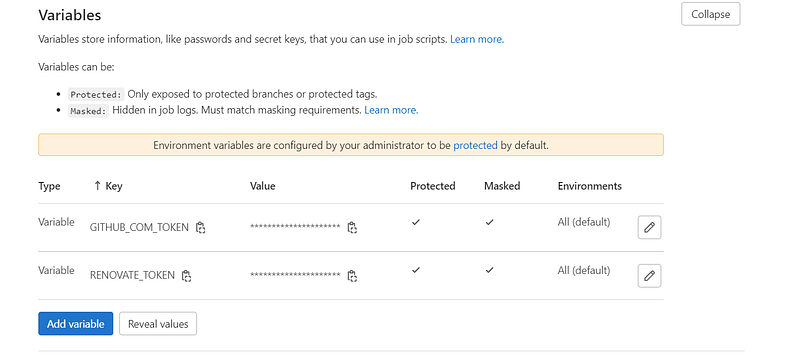
Renovate Bot operates on a schedule initiated by GitLab Pipelines. Before executing the pipelines, ensure that the tokens are set in the pipeline variables section. Retrieve the GitLab token from the service account created earlier and assign it to the variable RENOVATE_TOKEN. The GitHub token should be set under a different variable name, GITHUB_COM_TOKEN.
The pipeline is configured to run at a specific interval, which you can set in the repository.
Additionally, in the GitLab pipeline templates, several common parameters are initially set as environment variables required before executing the pipelines.
To enable the Renovate Bot to scan for dependency updates in a new repository, simply add the service account as a member with at least 'Developer' permission, as it requires this to create MRs. When the GitLab pipeline runs, it intelligently reviews the repositories it has access to and checks for any updates.
Exploring renovate.json5
The renovate.json5 file outlines the rules that instruct the Renovate Bot to look for any newly available updates for your libraries, plugins, or extensions. Below is a sample configuration:
{
"extends": ["github>renovatebot/.github"],
"prCreation": "immediate",
"automergeType": "pr",
"packageRules": [
{
"matchPackageNames": ["renovate"],
"automerge": true,
"separateMinorPatch": false,
"stabilityDays": 0
},
{
"description": "Do not pin package.json deps",
"matchFiles": ["package.json"],
"rangeStrategy": "replace"
}
]
}
- $schema: This imports the default schema into the rule file. You can find the defaults by following the provided URL.
- extends: Use this to reference a sharable and reusable config preset. More information can be found in the Renovate documentation.
- prCreation: Specifies when to create a Pull Request/Merge Request for the branch.
- automergeType: Determines whether to automatically merge branches/PRs without manual intervention.
There are numerous configurations that can be added to the rule file, which can be explored in detail in the Renovate documentation. The packageRules section allows you to define specific rules, with syntax varying by library, enabling you to tailor them to your needs.
Conclusion
In summary, the Renovate Bot is a tremendous asset and a significant time saver for developers. It streamlines the maintenance process by routinely checking repositories for new dependency updates across various systems like Terraform providers, Jenkins plugins, Python libraries, Golang modules, and Docker files, updating them as necessary. The potential is vast, and I look forward to further exploring its capabilities. I hope you find this article helpful, and I welcome any feedback.
For inquiries, feel free to connect with me through the following platforms:
- Medium
References

Inserted YouTube Videos
Forwarding Frontend Dependencies with Renovate Bot - YouTube
This video walks through the process of configuring Renovate Bot to manage frontend dependencies effectively.
Using Renovate to keep your version dependencies updated - Christian Hörl, SysEleven
In this video, Christian discusses how to utilize Renovate for maintaining updated version dependencies, providing valuable insights for developers.